DNS Georouting is the ability to send clients to a specific country and/or server based on geographical data. This allows:
- sending clients to a server that is closer to them, improving SEO
- using specific servers to publish contents and applications based on a specific continent, country or region
- implementing a robust geographical steering with full failover capabilities, to guarantee that your services are always available even in case of server/datacenter failures or maintenance
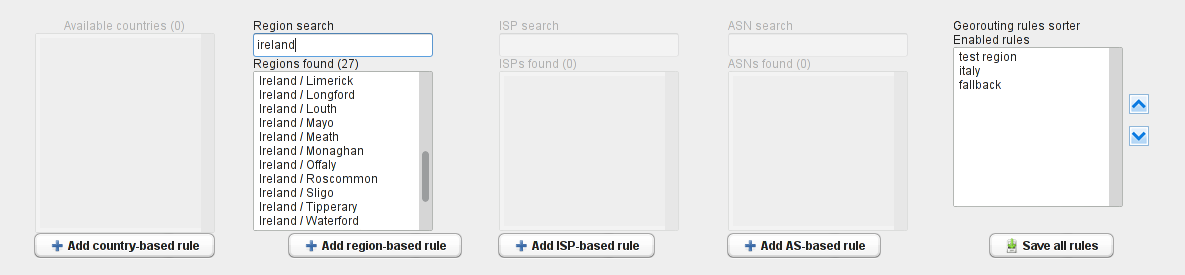
DNS Georouting allows you to define sets of rules to steer clients based on:
- Country of origin
- Region of origin
- Autonomous System Numbers (ASN)
- Internet Service Provider (ISP)
Each rule allows you to define a primary and a secondary list of servers (called targets in GSLB.me parlance). The primary list is used when there is at least one primary server available. The fallback list is used to direct clients to alternate servers in case all primaries are unavailable. Primary and fallback lists support their own balancing algorithm: this enables a powerful, easy to configure, DNS georouting infrastructure.
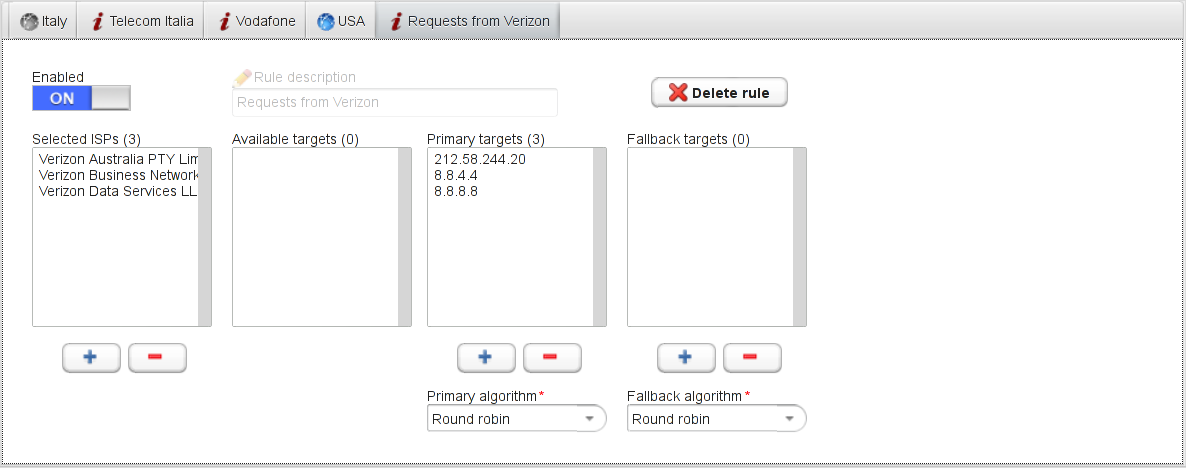
 Primary and fallback targets are automatically geo-positioned, enabling fast rollout of your geo-routed services.
Primary and fallback targets are automatically geo-positioned, enabling fast rollout of your geo-routed services.
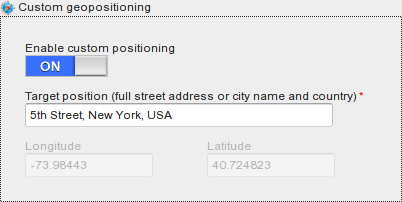
For additional flexibility you can enable custom geopositioning to manually define where your servers are, based on their geographical position.
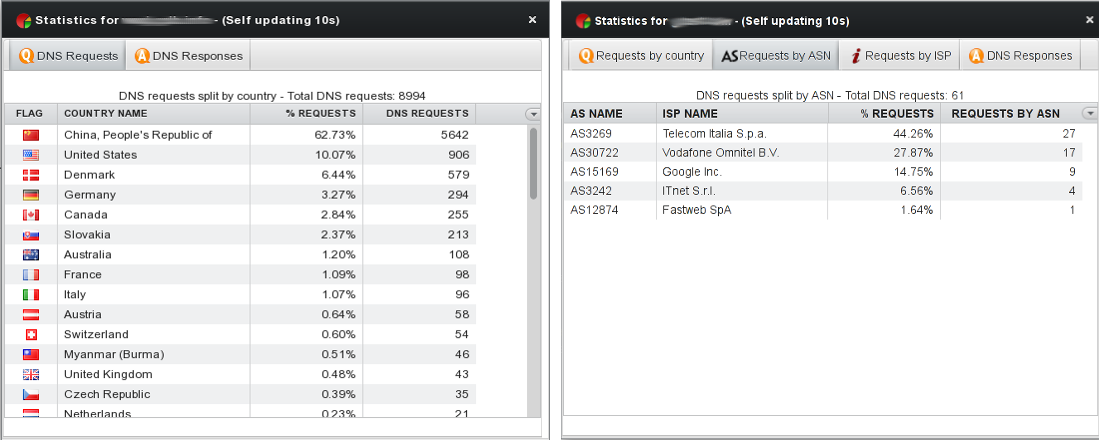
Statistics and Analytics
Real-time statistics provide a detailed view on all the statistics you need to keep your services under control, including:
- requests per country
- requests per autonomous system number (ASN)
- requests per Internet service provider (ISP)
- responses per target
In addition to DNS georouting, GSLB.me also supports proximity balancing, where targets are selected based on their vicinity to the requesting client.
Learn how to configure DNS georouting by reading our howto.
